
With increasing number of mobile phones, wireless and IoT devices production annually, and considering the high frequency, small size and the integration level of the components and 5G devices, the conventional conducted RF testing is not possible anymore. In addition, with implementation of the 5G systems, MIMO and steerable antenna, Over-the-air testing (OTA) has become an inevitable production test option.
What is OTA?
 Over-the-Air (OTA) Testing is a method for evaluating and predicting the performance and reliability of an RF wireless device or system. The DUT (Device Under Test) is placed in a test chamber, to simulate the real-life situation. The device is considered in different scenarios to investigate how it responds to different conditions. OTA testing enables us to check the performance of the device or system, by measuring its entire signal path and antenna performance.
Over-the-Air (OTA) Testing is a method for evaluating and predicting the performance and reliability of an RF wireless device or system. The DUT (Device Under Test) is placed in a test chamber, to simulate the real-life situation. The device is considered in different scenarios to investigate how it responds to different conditions. OTA testing enables us to check the performance of the device or system, by measuring its entire signal path and antenna performance.
These tests are very important for any devices or systems, since their intended performance might be affected when they are placed in the real world, with some other devices and components in their proximity, as they all affect the radiation pattern in the area. For example, a mobile phone with poorly placed antenna may suffer from low signal, when a consumer holds it the wrong way.

OTA is an essential test for any mobile phone, tablet or IoT devices, since any component could degrade their performance. They are also compulsory for some product certification to set standards. As it is evident that OTA is vital in different stages of a product development, from R&D, prototyping, testing, certification and mass production.
Conducted RF Testing Vs. OTA
Traditionally conducted testing was used to verify the devices or systems performance. One problem with conducted testing was that they do not include the effects of the wireless radiation field. On the other hand, OTA testing, which is also known as radiated testing, in comparison with conducted testing, has the advantage that there is no need to break or modify the radio device for testing.
 Testing new systems and devices, such as 5G and SATCOM, is no longer viable with conducted testing, due to a number of reasons, including the integration of the antenna to the board and complexity level of the system architecture. In some cases, due to lack of the connector for the antenna, the testing is exclusively possible with OTA in 5G high frequency bands.
Testing new systems and devices, such as 5G and SATCOM, is no longer viable with conducted testing, due to a number of reasons, including the integration of the antenna to the board and complexity level of the system architecture. In some cases, due to lack of the connector for the antenna, the testing is exclusively possible with OTA in 5G high frequency bands.
OTA Implementation
Various approaches have been reported in the literature for OTA implementation, including Direct Far-Field, Indirect Far-field (using component ranges) and Near-Field in which a near-field to far-field is used for transformation. The issue with these methods lie on speed, accuracy and cost.
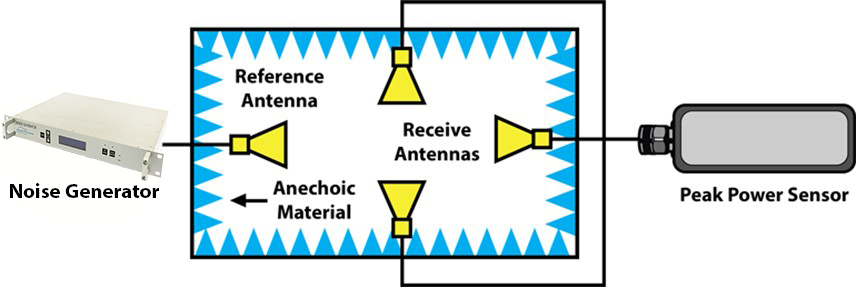
Recently a new approach has been proposed which is simpler in implementation, faster and more cost-effective. In this method, a noise generator is used to produce a signal to simulate the multi-tone signal in the real-world scenario. An schematic of this approach is shown in the Figure.
Atlantic Microwave Noise Generators
Manual Broadband Noise Generators provide up to 1 watt of white Gaussian noise output in several models over the 10Hz to 18GHz frequency range and are designed to be used either as laboratory instruments or as built-in system test facilities. The noise, which is diode generated, is amplified and the level can be varied in 1dB steps from 0 to 10dB or optionally in 0.1dB steps from 0 to 101dB.
Ethernet Controlled Noise Generators provide up to 1 watt of white Gaussian noise output in several models over the 10Hz to 18GHz frequency range, with custom options to 40GHz and are designed to be used either as laboratory instruments or as built-in system test facilities. The noise, which is diode generated, is amplified and the level can be varied in steps from 0 to 60dB depending upon the attenuator range option chosen. Control of the output level is via a remote GUI and can also be affected locally with the front panel controls and LCD screen.

Further standard options are available in addition to the ability to provide custom solutions for applications.
- Analogue/digital
- Manual/remotely control
- Various frequency coverage to cover the 5G band



